บทความนี้ถูกย้ายมาจาก blog เก่าของผมบน Medium แต่ได้ถูกปรับปรุงและเรียบเรียงเนื้อหาใหม่แล้ว
Table of Contents#
- บทนำ (Introduction)
- Kubernetes Services คืออะไร?
- ชนิดของ Kubernetes Services (Recap สั้น ๆ)
- [V.1] ลอง Deploy Application (ในใจ) โดยใช้แค่ Services
- Kubernetes Ingress คืออะไร?
- [V.2] ลอง Deploy Application (ในใจ) โดยใช้ Ingress คู่กับ Services
- บทสรุป (Conclusion)
บทนำ (Introduction)#
บทความนี้เหมาะสำหรับผู้ใช้ Kubernetes มือใหม่หรือคนที่กำลังสับสนว่า Kubernetes Services กับ Kubernetes Ingress ต่างกันยังไง ผมจะอธิบายโดยยกตัวอย่าง application ขึ้นมาลอง deploy ในใจ เริ่มจากแบบที่ “ไม่ใช้ Ingress” และ “ใช้ Ingress” เพื่อให้ทุกคนเห็นความแตกต่างและเข้าใจว่า Kubernetes Ingress เข้ามาช่วยอะไร
Kubernetes Services คืออะไร?#
Kubernetes Services คือ endpoint หรือ interface ที่เราสร้างขึ้นให้กับ pod หรือกลุ่มของ pods ที่ทำงานประเภทเดียวกันอยู่ (service เดียวกัน) พูดง่าย ๆ มันคือประตูขาเข้านั่นแหละครับ
การสร้าง service จึงเป็นการสร้างประตูหรือช่องทางให้ traffic จากข้างนอกสามารถเข้ามาพูดคุยกับ pod กลุ่มนั้นได้ง่ายขึ้นโดยไม่เจาะจงว่าเป็น pod ไหนในกลุ่มนั้น ๆ เพราะ service จะเป็นคนจัดการให้
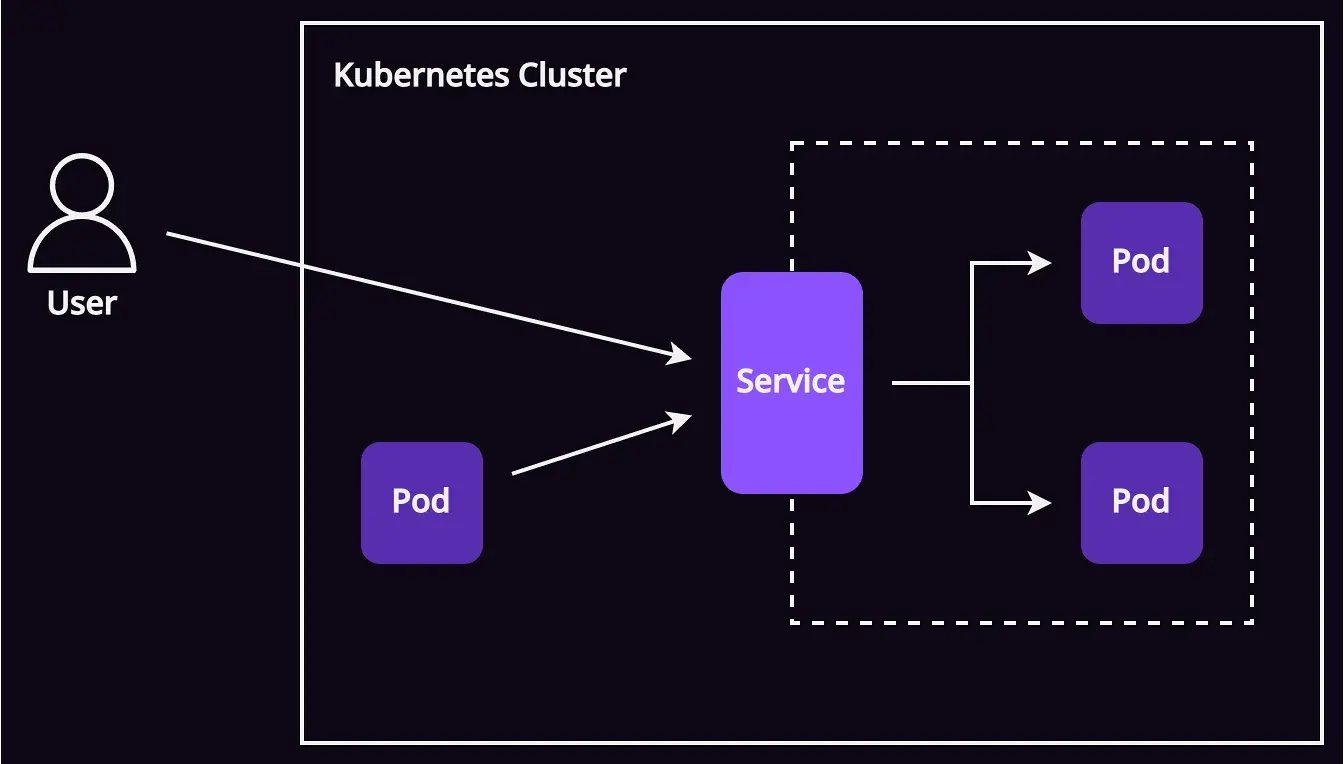
ลองคิดถึงเบอร์โทรศัพท์ 191 ว่าเป็น service ก็ได้ครับ ซึ่งเป็นเบอร์ที่เราทุกคนรู้ว่ามันใช้โทรหาตำรวจ โดยตำรวจเองก็อาจจะมีหลายนาย เทียบเป็น pod ก็คือมีหลาย pod
ในมุมประชาชน (เทียบกับ user) เราไม่จำเป็นต้องรู้ชื่อ (เทียบกับ DNS name ของ pod) หรือหมายเลขประจำตัว (เทียบกับ IP ของ pod) ของตำรวจแต่ละนาย เราไม่สนว่ามีตำรวจกี่นายที่กำลังทำงานอยู่หรือใครบ้างที่ลาในวันนั้น (จำนวนของ pods)แต่ถ้าเราต้องการจะโทรหาตำรวจก็แค่โทรไปที่ 191
ชนิดของ Kubernetes Services (Recap สั้น ๆ)#
1. ClusterIP Service#
เมื่อเราสร้าง ClusterIP service ขึ้นมา Kubernetes จะสร้าง virtual IP ให้กับ service นั้นโดยใช้ IP จาก pool ที่ reserve ไว้ใน cluster ทำให้ pods อื่น ๆ ภายใน cluster สามารถเข้าถึง service นี้ได้ผ่าน IP ที่สร้างขึ้น แต่ traffic จากข้างนอกจะไม่สามารถเข้าถึง service ชนิดนี้ได้
เหมาะสำหรับ expose service ที่ต้องการการเข้าถึงจาก pod ภายใน cluster ด้วยกัน เช่น
- backend service ที่ต้องการให้ frontend เข้ามาคุย
- database service ที่ต้องการให้ backend เข้ามาคุย
ตัวอย่าง ClusterIP Service Manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-clusterip-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
2. NodePort Service#
เมื่อเราสร้าง NodePort service ขึ้นมา Kubernetes จะ reserve port หนึ่งขึ้นมาบน node ทั้งหมดใน cluster (ใช้ port 30000–32767) และทำให้ traffic ที่ส่งมาที่ node IP ผ่าน port นั้น (<NodeIP>:<NodePort>) จะถูกส่งเข้ามายัง service ที่เราสร้างขึ้น โดยจะส่งผ่าน IP ของ node ใดก็ได้ แต่ต้องอยู่ใน network เดียวกับ Kubernetes node เช่น
สมมุติ IP ของ node ใน cluster เป็น
- Node A: 10.1.1.100
- Node B: 10.1.1.200
และผมมี NodePort อยู่ 2 services ซึ่งกำหนดให้ใช้ port ตามนี้
- Shopping cart ใช้ port 30001
- Product catalog ใช้ port 30002
ดังนั้น
- Traffic ที่ส่งไปที่ IP 10.1.1.100 (Node A) ด้วย port 30001 จะไปหา shopping cart service
- Traffic ที่ส่งไปที่ IP 10.1.1.200 (Node B) ด้วย port 30001 ก็จะไปหา shopping cart service
และ
- Traffic ที่ส่งไปที่ IP 10.1.1.100 (Node A) ด้วย port 30002 จะไปหา product catalog service
- Traffic ที่ส่งไปที่ IP 10.1.1.200 (Node B) ด้วย port 30002 ก็จะไปหา product catalog service
NodePort เหมาะสำหรับใช้ expose service ที่ต้องการให้เข้าถึงได้จากภายนอก cluster แต่ยังคงต้องอยู่ใน network เดียวกัน เช่น
- ต้องการให้ user ใน office เข้าถึง service เพื่อ test ระหว่างการพัฒนา application
- หรือเป็น service ที่ใช้งานได้เฉพาะ network ภายในองค์กร (ไม่ได้เข้ามาจาก internet นะครับ)
ตัวอย่าง NodePort Service Manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-nodeport-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 30001
3. LoadBalancer Service#
เมื่อเราสร้าง LoadBalancer service ขึ้นมา Kubernetes จะ call API ไปสร้าง load balancer จริง ๆ ขึ้นมานอก cluster (ถ้าใช้ cloud มันก็สร้างขึ้นมาบน cloud platform ส่วน on-premise ก็ต้องเตรียม solution เอาไว้รองรับด้วย) ทำให้ user จากข้างนอกสามารถเข้าถึง service ผ่าน load balancer IP ได้ (ต่างกับ NodePort ตรงที่ไม่ได้ใช้ IP ของ Kubernetes node)
LoadBalancer เหมาะสำหรับใช้ในการ expose service ที่ต้องการให้ user จากข้างนอก Kubernetes cluster หรือจาก internet สามารถเข้าถึงได้ เช่น ใช้กับ web application เป็นต้น
ตัวอย่าง LoadBalancer Service Manifest
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-loadbalancer-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
[V.1] ลอง Deploy Application (ในใจ) โดยใช้แค่ Services#
สมมุติผมมี e-commerce application ซึ่งประกอบด้วย 4 ส่วน ได้แก่
- Frontend
- Product Catalog
- Shopping Cart
- Postgres Database
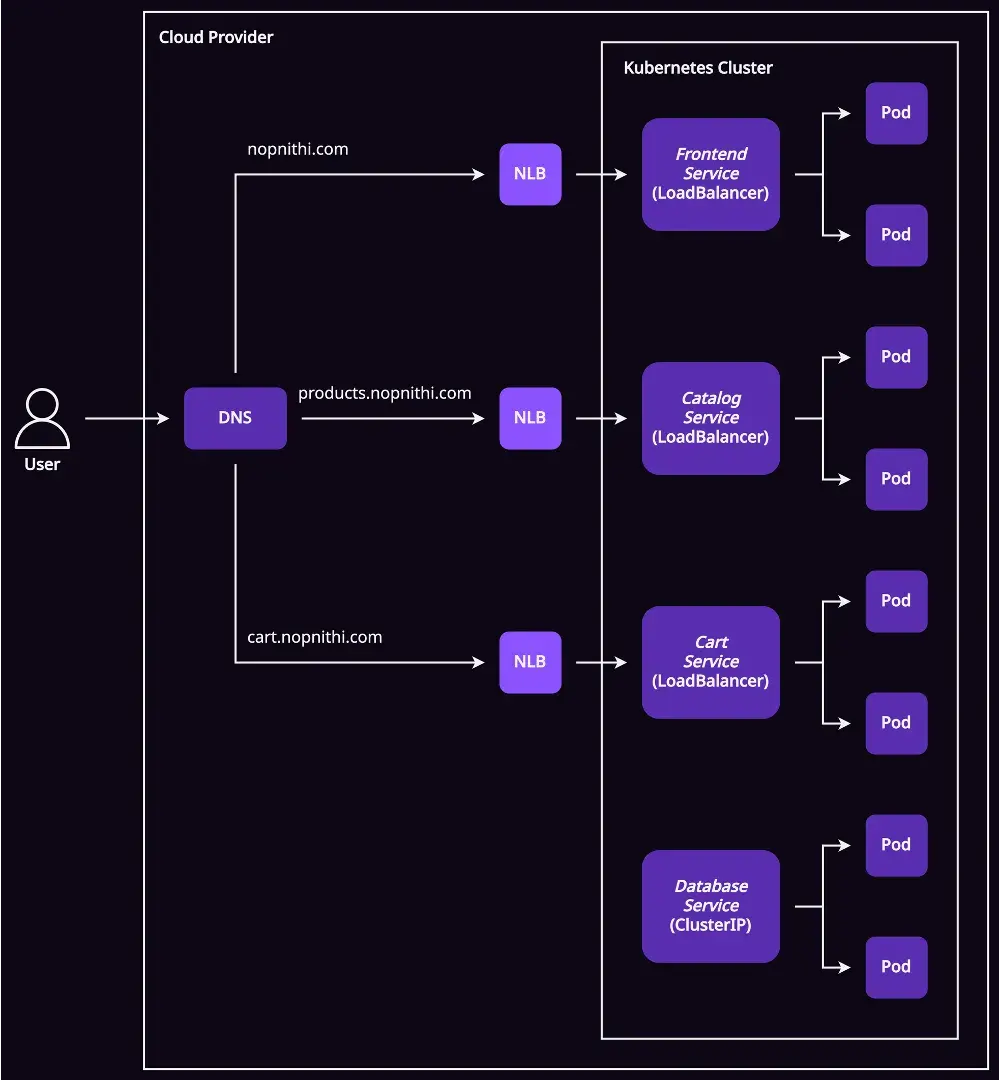
ถ้าผมจะ deploy application นี้บน Kubernetes ผมก็อาจจะเลือกใช้ services ดังนี้
- Frontend ใช้
LoadBalancerservice เพราะมี user จาก internet เรียกเข้ามา - Product catalog ใช้
LoadBalancerservice เพราะมี user จาก internet เรียกเข้ามา - Shopping cart ใช้
LoadBalancerservice เพราะมี user จาก internet เรียกเข้ามา - Postgres database ใช้
ClusterIPservice เพราะถูกเรียกจาก service ข้างใน cluster เท่านั้น
อันนี้แค่ยกตัวอย่างนะครับ เพราะในความเป็นจริง product catalog service หรือ shopping cart service อาจจะไม่ได้ถูก expose ตรงไปหา user (อยู่หลัง frontend อีกที) ตรงนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับ design ของแต่ละ app
ตัวอย่าง Manifest สำหรับ Application V.1#
# Frontend Service (LoadBalancer)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: frontend
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: frontend
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
# Product Catalog Service (LoadBalancer)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: product-catalog
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: product-catalog
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
# Shopping Cart Service (LoadBalancer)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: shopping-cart
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: shopping-cart
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
# Postgres Database Service (ClusterIP)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: postgres
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: postgres
ports:
- port: 5432
targetPort: 5432
และผมจะต้องสร้าง A record บน DNS ข้างนอกแบบนี้
nopnithi.comชี้ไปหา load balancer IP ของ frontend serviceproducts.nopnithi.comชี้ไปหา load balancer IP ของ catalog servicecart.nopnithi.comชี้ไปหา load balancer IP ของ cart service
ปัญหาการ Deploy Application โดยใช้แค่ Kubernetes Services#
- เปลือง: ต้องเสียค่า load balancer ถึง 3 ตัว
- ยุ่งยาก: ต้องจัดการ DNS record ถึง 3 records
- ยุ่งยาก: ถ้า load balancer IP เปลี่ยนก็ต้องแก้ DNS record ใหม่ (ถ้าใช้ cloud แก้ง่ายหน่อย)
- ยุ่งยาก: ต้องทำ SSL/TLS termination ที่ NLB ทั้ง 3 ตัว
- มีข้อจำกัด: ไม่สามารถทำ URL path routing ได้ ต้องใช้ subdomain แทน (ยกเว้นตั้ง proxy ขึ้นมาเอง)
และนั่นเป็นเหตุผลที่ Kubernetes Ingress จะมาช่วยเรา…
Kubernetes Ingress คืออะไร?#
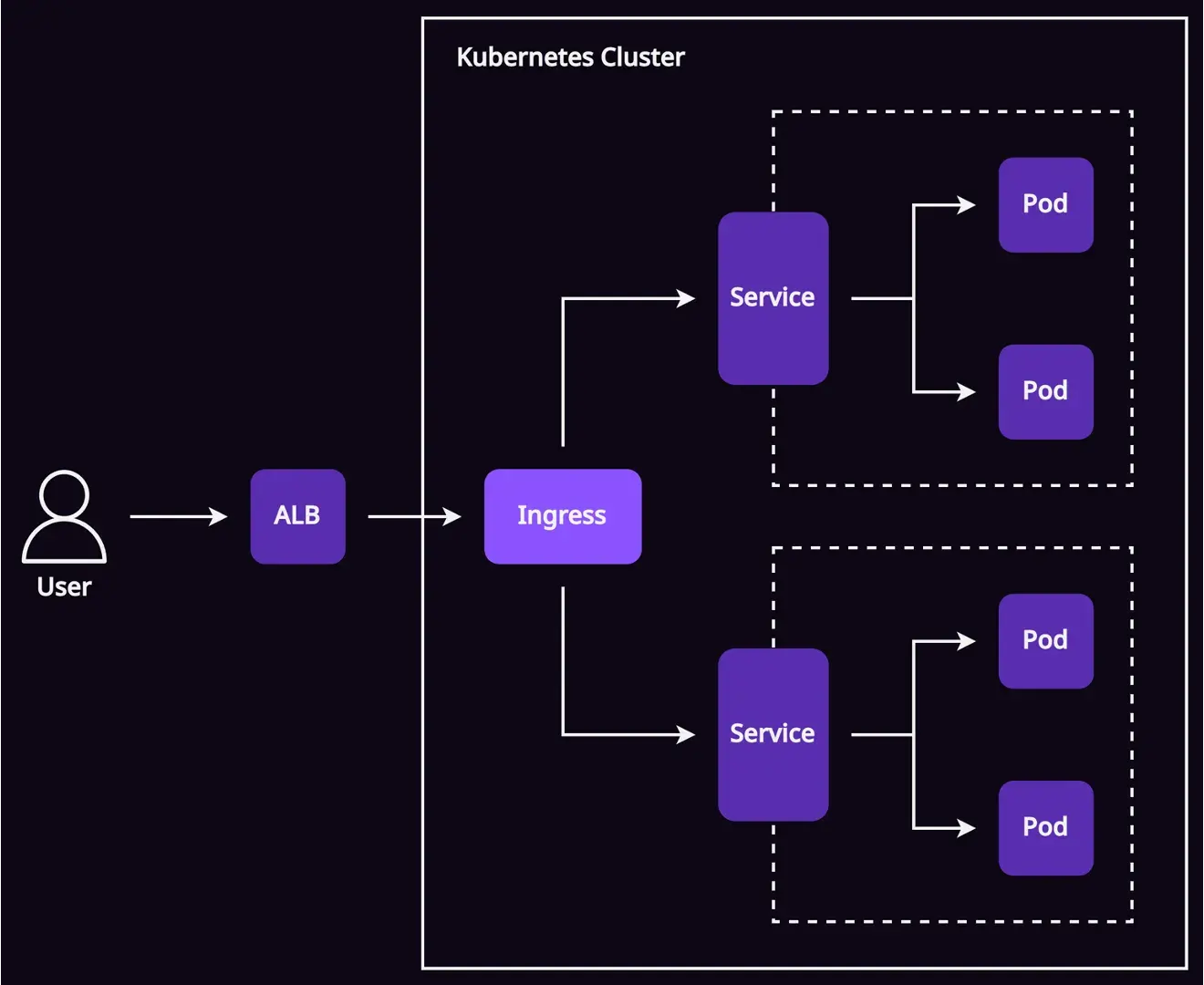
Kubernetes Ingress คือ traffic controller ซึ่งมาแทรกอยู่ด้านหน้า services อื่น ๆ ทำหน้าที่รับ traffic จาก load balancer แล้วส่ง traffic ให้ service ต่าง ๆ ตาม routing rules
การจะใช้ Ingress ต้องมี 2 ส่วน (ผมจะไม่ได้ลงรายละเอียดนะครับ)
- Ingress Controller: ต้อง deploy controller ก่อน เช่น NGINX, Traefik, HAProxy, หรืออื่น ๆ
- Ingress Resource: ต้องสร้าง Kubernetes resource ขึ้นมา ก็เหมือนกับ pods หรือ deployments นั่นแหละ
[V.2] ลอง Deploy Application (ในใจ) โดยใช้ Ingress คู่กับ Services#
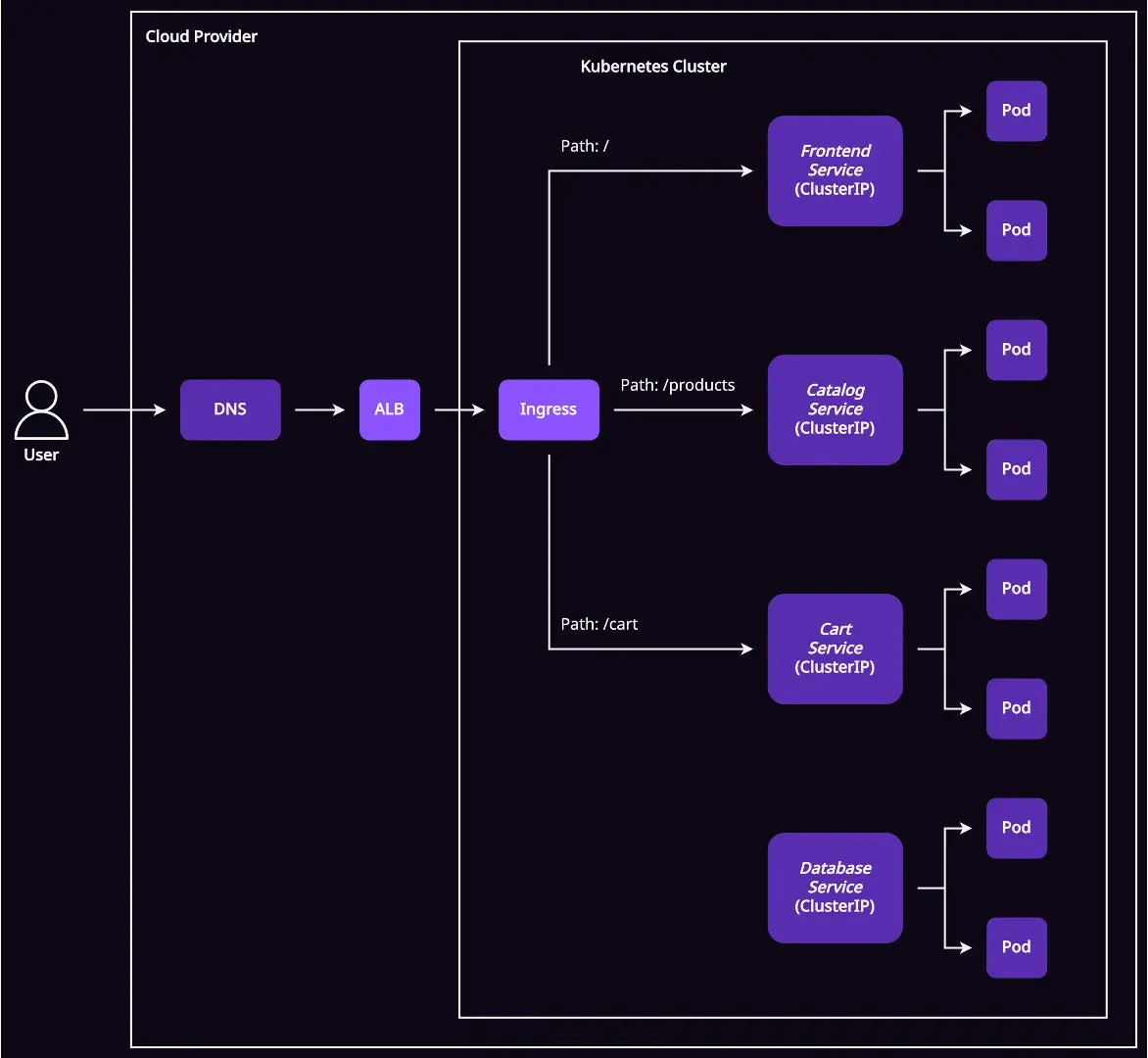
ในเวอร์ชั่นนี้ผมจะเปลี่ยน services ทั้ง 3 ตัวจาก LoadBalancer เป็น ClusterIP ให้หมด เพราะสิ่งที่จะมาคุยกับมันคือ ingress และอยู่ภายใน cluster เหมือนกัน และจะใช้ load balancer จาก ingress ตัวเดียวในการ expose ออกไปข้างนอก cluster
ตัวอย่าง Service Manifest สำหรับ Application V.2#
# Frontend Service (ClusterIP)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: frontend-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: frontend
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
# Product Catalog Service (ClusterIP)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: catalog-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: product-catalog
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
# Shopping Cart Service (ClusterIP)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: cart-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: shopping-cart
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
# Postgres Database Service (ClusterIP)
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: postgres-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: postgres
ports:
- port: 5432
targetPort: 5432
ตัวอย่าง Ingress Manifest สำหรับ Application V.2#
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nopnithi-shop-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- host: nopnithi.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: frontend-service
port:
number: 80
- path: /products
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: catalog-service
port:
number: 80
- path: /cart
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: cart-service
port:
number: 80
ส่วน DNS record จาก 3 records ก็จะเหลือแค่ตัวเดียว โดยชี้ไปหา load balancer IP ของ ingress
nopnithi.comชี้ไปที่ load balancer IP ของ ingress
สิ่งที่ได้หลังจากนำ Ingress เข้ามาช่วย#
- จากที่ต้องใช้ load balancer 3 ตัว ก็เหลือ 1 ตัว
- จัดการ DNS record เดียว โดยชี้มาที่ ingress
- สามารถทำ routing จาก URL path ได้
- จัดการ configuration ของ URL routing หรือ SSL/TLS ที่ ingress จุดเดียว
บทสรุป (Conclusion)#
หากมองผิวเผินอาจจะรู้สึกว่า Kubernetes services กับ Kubernetes ingress นั้นคล้ายกัน แต่ความเป็นจริงนั้นต่างกัน และ ingress ไม่ได้มาแทนที่ services แต่มาเพื่อช่วยเสริมการทำงานให้
โดยเราอาจเลือกใช้แค่ services ก็ได้ ถ้า…
- Service นั้นติดต่อกันแค่ภายใน
- ต้องการเข้าถึง service แค่เพื่อ test หรือ debug ในขั้นตอนพัฒนา
- หรือมี service เดียวที่ต้องการ expose ให้ user จาก internet เข้าถึงได้
แต่เมื่อใดก็ตามที่เรามีหลาย ๆ service ที่ expose ออกไปข้างนอกและต้องการจัดการ URL path routing หรือ SSL/TLS certification ทั้งหมดจากที่เดียว ตรงนี้ Kubernetes Ingress จะเข้ามาช่วยได้ และใช่ครับ…ส่วนมากเราก็มักจะได้ใช้ Ingress กันอยู่แล้วแหละ 😂